In the rapidly evolving field of advanced drug and nutrient delivery systems, co-loading liposomes have emerged as a groundbreaking technology, and the integration of rare ginsenosides as a core membrane material has further elevated their performance and application potential. Derived from ginseng plants as secondary metabolic saponins (with a natural content of less than 0.001% even after refined extraction), rare ginsenosides bring multiple synergistic advantages to co-loading liposomes, transcending the limitations of traditional liposomal formulations (which typically rely on phospholipids and cholesterol) and opening up new horizons for pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and nutritional supplement industries.
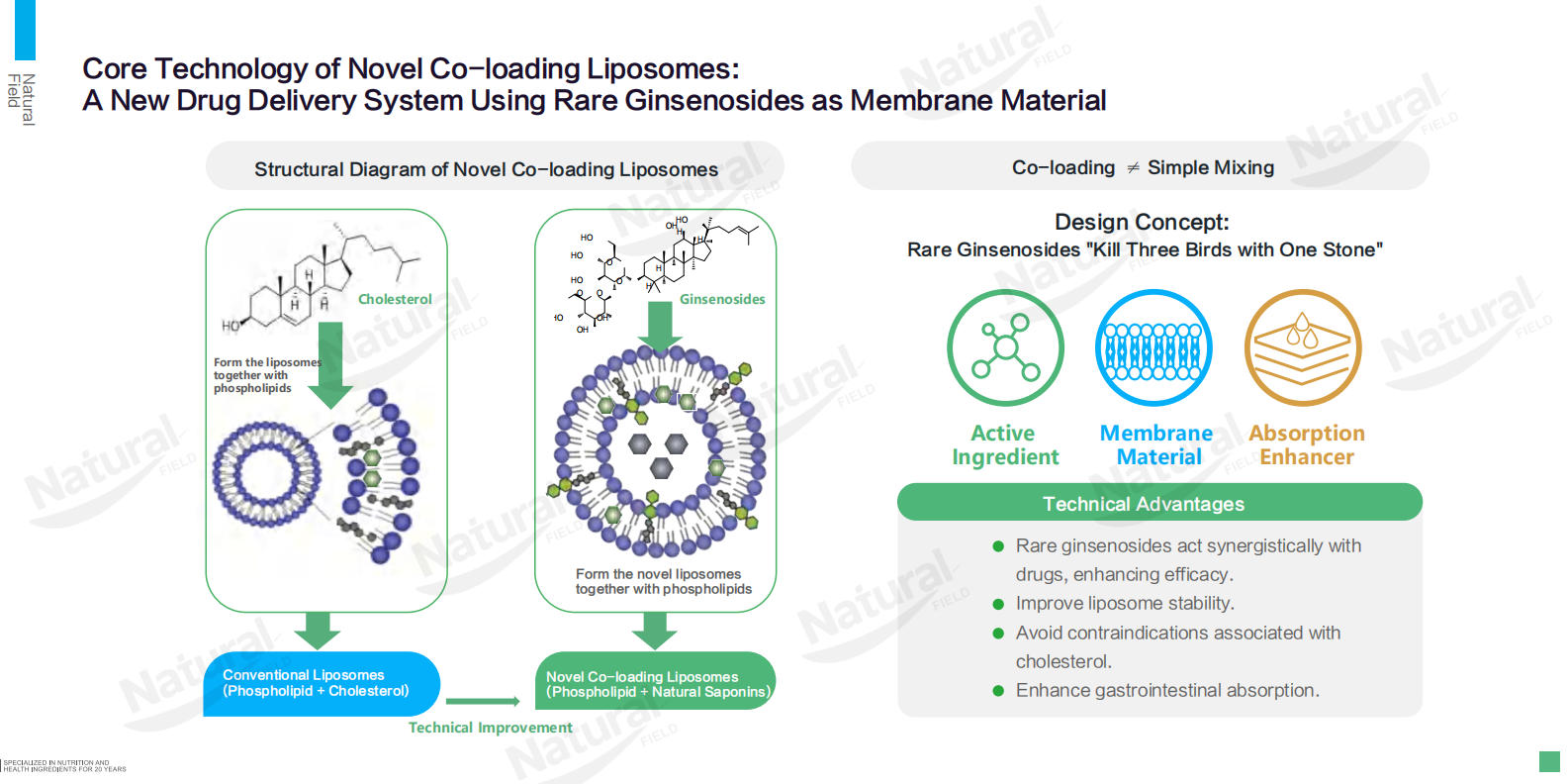
Traditional liposomes rely on cholesterol to regulate membrane fluidity and stability, but this component may pose contraindications for specific populations (e.g., those with cardiovascular concerns) and offers no inherent biological activity. Rare ginsenosides (including diol-type and triol-type variants such as Rg3, Rh2, Rk2, and Rh4) address these drawbacks by functioning as both membrane-structuring agents and bioactive ingredients. When combined with phospholipids to form co-loading liposomes, they not only replicate cholesterol’s membrane-stabilizing effects but also introduce inherent therapeutic benefits. This "three-in-one" design—structural support, stability enhancement, and biological activity—redefines the role of membrane materials in liposomal systems, making the formulation more versatile and compatible with a broader range of consumer needs.
Rare ginsenosides exhibit excellent liposome-forming ability, a critical advantage over prototype ginsenosides which lack effective membrane-forming properties. Diol-type and triol-type rare ginsenosides interact synergistically with phospholipids to form uniform, nanoscale vesicles (50–100 nm in average particle size), far smaller than micron-sized traditional liposomes (10–30 μm). This nanoscale structure ensures consistent particle size distribution and granularity, a key prerequisite for standardized production and quality control. Experimental data from Natural Field confirms that co-loading liposomes incorporating rare ginsenosides maintain stable physicochemical properties, with encapsulation efficiencies exceeding 90% for liposoluble components and 60% for water-soluble ingredients—outperforming many conventional liposomal formulations. This stability extends the shelf life of products and preserves the activity of encapsulated ingredients during storage and gastrointestinal transit.
One of the most significant advantages of rare ginsenosides in co-loading liposomes is their ability to enhance oral bioavailability, a longstanding challenge in lipid-based delivery. Two key mechanisms drive this improvement:
Bypassing Efflux Transporters: Rare ginsenosides such as 20(S)-Rg3 inhibit intestinal efflux transporters (e.g., P-gp and BCRP), which normally pump absorbed substances back into the gut lumen, reducing bioavailability. This inhibition allows co-loading liposomes to bypass these barriers and accumulate more effectively in enterocytes.
Facilitated Cellular Uptake: The nanoscale structure of rare ginsenoside-based liposomes enables efficient penetration of intestinal epithelial cells. In vitro Caco-2 cell experiments demonstrate that co-loading liposomal Coenzyme Q10 achieves a 7.86-fold higher cumulative transport than free Coenzyme Q10, and 2.21-fold higher than conventional liposomes. Similarly, co-loading liposomal glutathione shows a 5.33-fold increase in relative absorption compared to free glutathione. In vivo studies in rats further validate these results: co-loading liposomes exhibit AUC values 2.0–7.7 times higher than free drugs and 1.8–4.5 times higher than traditional liposomes, depending on the encapsulated ingredient (e.g., NMN, creatine, and curcumin).
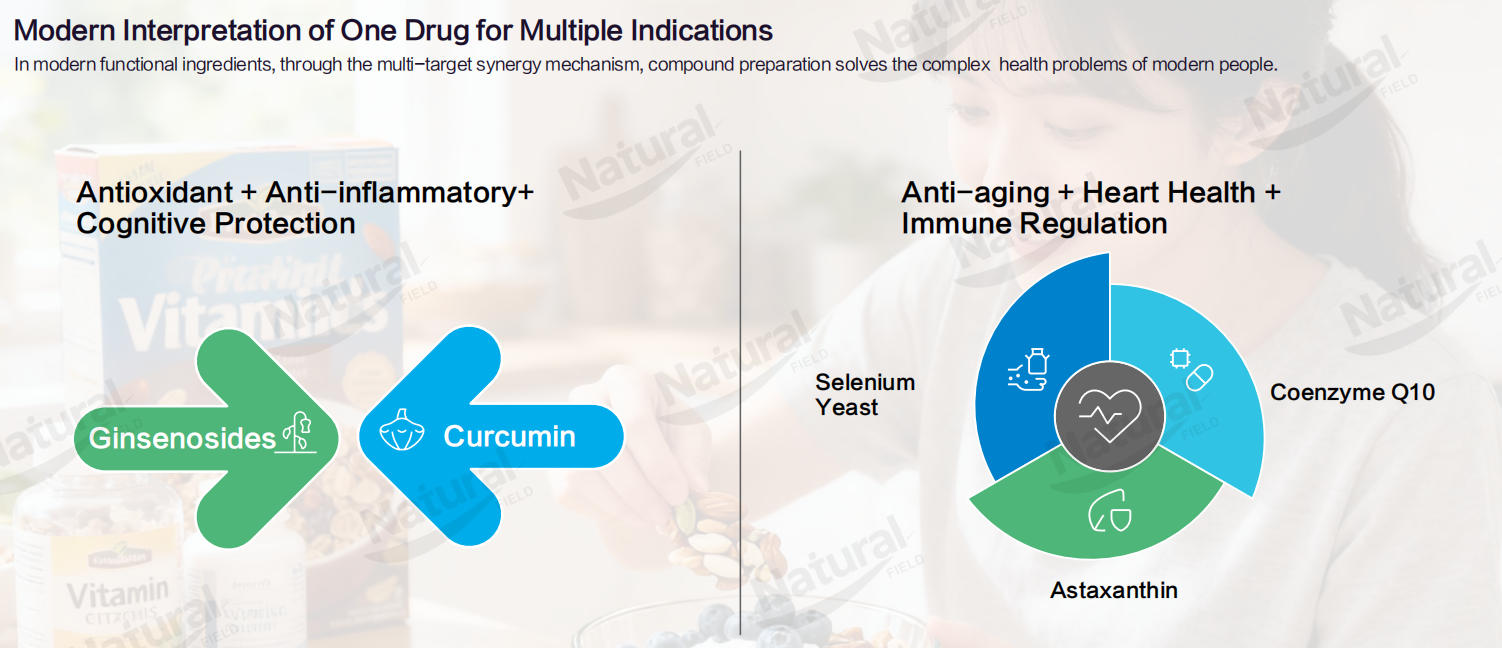
Unlike inert membrane materials, rare ginsenosides possess well-documented bioactivities that synergize with encapsulated ingredients, amplifying the overall efficacy of co-loading liposomes. Their core functions include immune enhancement, anti-aging, anti-radiation, anti-wrinkle, and moisturizing effects. When combined with ingredients such as Coenzyme Q10 (cardiovascular health), curcumin (anti-inflammatory), or glutathione (antioxidant), rare ginsenosides create a synergistic effect that addresses complex health needs. For example:
Co-loading liposomal Coenzyme Q10 significantly reverses D-galactose-induced weight loss in mice, upregulates spleen and thymus indices, and increases IgG/IgM levels—effects attributed to the synergistic anti-aging and immune-boosting properties of Coenzyme Q10 and rare ginsenosides.
Co-loading liposomal curcumin outperforms 10% water-soluble curcumin in alleviating colitis symptoms in mice, reducing colon inflammation and spleen congestion through the combined anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin and rare ginsenosides.
This synergism aligns with the global trend toward compound formulations in health products, where multi-targeted solutions are increasingly preferred over single-function ingredients.
Rare ginsenosides’ versatility extends to diverse product formats and application fields. Triol-type rare ginsenosides are ideal for co-loading liposomes in solid beverages (e.g., glutathione-based gut-skin support products), while diol-type variants excel in capsule formulations (e.g., Coenzyme Q10 supplements). Beyond nutritional supplements, these liposomes are also applicable in cosmetics (enhancing skin penetration and anti-aging efficacy) and pharmaceuticals (improving the delivery of poorly soluble or unstable drugs).
Moreover, rare ginsenoside-based co-loading liposomes meet key market demands: they cater to the preference for "high absorption" and "high bioavailability" products driven by rising consumer health awareness, and align with policy dividends supporting high-end and compound formulations in China and the U.S. Their compatibility with liquid, capsule, and powder dosage forms—along with e-commerce and DTC sales channels—further enhances their market competitiveness.
Rare ginsenosides have transformed co-loading liposome technology from a mere delivery system into a synergistic therapeutic platform. By combining structural support, stability enhancement, absorption promotion, and inherent biological activity, they address critical limitations of traditional liposomes while unlocking new value for pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and nutritional products. As research into rare ginsenosides and co-loading technology deepens, their role in advancing precision nutrition and targeted delivery will continue to expand, offering innovative solutions for global health and wellness needs. The data-backed advantages of rare ginsenosides—superior stability, enhanced bioavailability, synergistic efficacy, and broad applicability—position them as a cornerstone of next-generation liposomal formulations.