Ashwagandha is often used in combination with other herbs and nutrients to maximize its health benefits while expanding its application scenarios in fields such as immune regulation, neurological health, and metabolic balance.
The synergistic formulation of Ashwagandha and magnesium holds significant value in the health sector. Ashwagandha can reduce cortisol levels by inhibiting the overactivation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and regulate neurotransmitters to improve sleep. Magnesium, on the other hand, modulates the activity of GABA receptors to assist in cortisol control, promotes melatonin synthesis to extend deep sleep duration, and participates in muscle cell metabolism to support muscle repair. A common formulation involves administering 300-600 mg of Ashwagandha extract (containing 30-40 mg of withanolides) daily, combined with 200-300 mg of magnesium glycinate or magnesium citrate (e.g., BIOGENA’s Ashwagandha Formula, which contains 500 mg of Ashwagandha extract and 70 mg of magnesium per capsule). This formulation is suitable for scenarios such as relieving anxiety in high-stress populations, improving sleep in middle-aged and elderly individuals, and promoting recovery in athletes.
Natural Field Bio-technique Co., Ltd. has developed a series of novel trace element supplements (including Ashwagandha acid-calcium, -magnesium, -zinc, and -iron) using patented technology. Furthermore, Ashwagandha acid liposomes prepared from these supplements significantly enhance in vivo bioavailability, and relevant research is currently ongoing.
In a study on obese mice induced by a high-fat diet, the complex of Ashwagandha and Chrysanthemum (ASC) exhibited a significant synergistic anti-obesity effect. Its ability to reduce the final body weight of mice and decrease the accumulation of total white adipose tissue (including subcutaneous and visceral fat) was significantly stronger than that of Ashwagandha or Chrysanthemum alone. Meanwhile, in terms of improving lipid metabolism, activating energy metabolism-related pathways (e.g., AMPK and UCP1 pathways), and regulating the expression of key adipogenic proteins (e.g., PPARγ and C/EBPα), the effect of ASC also exceeded that of individual components. ASC exerts its anti-obesity effect by synergistically regulating metabolism-related processes [1].
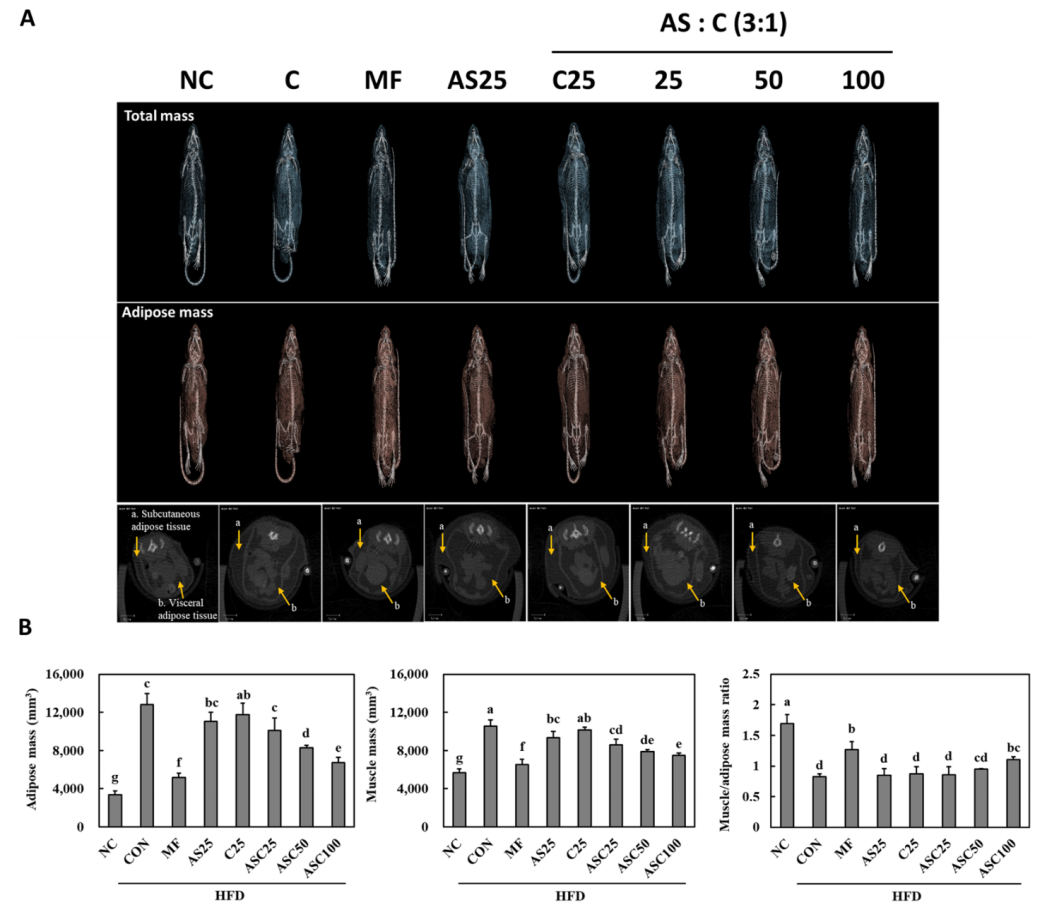
Figure 3 The effect of ASC complex on fat and muscle mass in HFD-induced obese mice [1]
A study used juvenile Labeo rohita (rohu) as the research object and added different proportions of a mixture of Ashwagandha root extract and vitamin C to their diet. By detecting hematological indicators (e.g., increased hemoglobin content and red blood cell count), immunological indicators (e.g., improved nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) reduction and lysozyme activity), biochemical indicators (e.g., decreased glucose content and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity), and the survival rate of juvenile fish under low pH and waterborne iron stress (e.g., the relative percentage survival under combined stress reached 65%, significantly higher than 0% in the control group), it was found that the mixture with a 1.0% addition amount could most effectively stimulate the immune response of juvenile fish, enhance their immune defense capabilities, and reduce damage caused by multiple stresses during a 15-day feeding period [15].
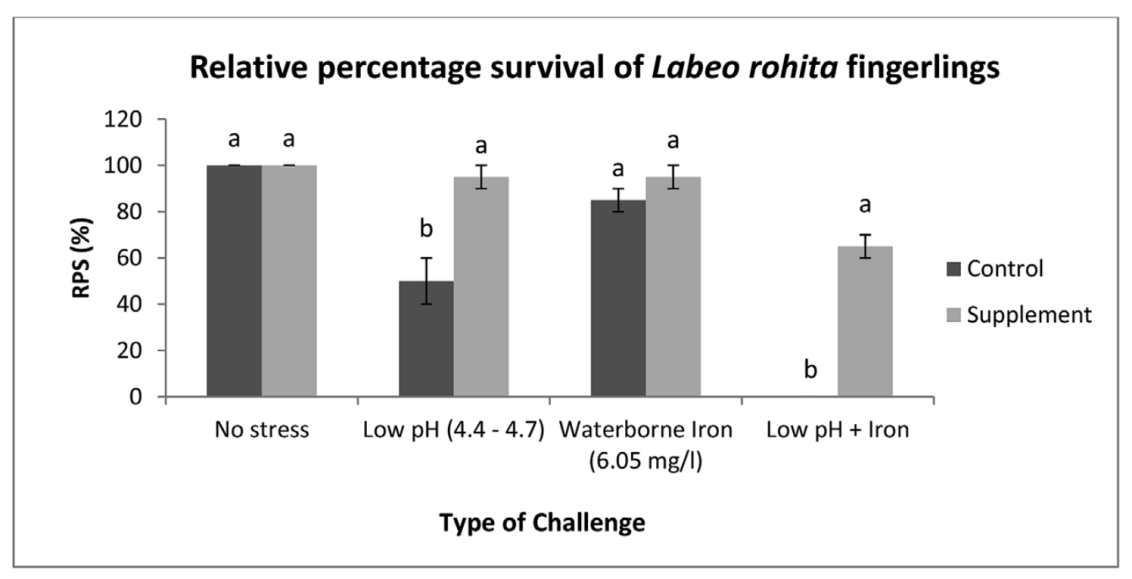
Figure 4 Relative survival rate of Labeo rohita fingerlings in the challenge experiment [2]
References:
[1]Park S-H, Park J, Yoo E, et al Withania somnifera and Chrysanthemum zawadskii Herbich var. latilobum (Maxim.) Kitamura Complex Attenuates Obesity in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5230.
[2]Laltlanmawia C, Saha RK, Saha H, Biswas P. Ameliorating effects of dietary mixture of Withania somnifera root extract and vitamin C in Labeo rohita against low pH and waterborne iron stresses. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 May;88:170-178.
 English
English français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español русский
русский português
português






